sm2mm pipelines
This page describes the file format for sm2mm pipelines and lists some useful ready-to-use examples.
Note
👉 There is an online graphical editor for sm2mm pipelines
1. What does sm2mm mean?
sm2mm stands for the process of transforming a “simple map” file, a “key-frame map” typically generated by a SLAM system and having the .simplemap extension, into a “metric map” file (.mm extension), typically comprising several map layers of different types, semantics, or serving to different purposes.
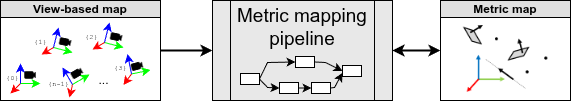
Users may use this through two interfaces: a CLI application sm2mm or the C++ API mp2p_icp_filters::simplemap_to_metricmap().
2. Pipeline file specification
Pipeline configuration files are written in YAML format and define the sequence of operations to be applied to the raw sensor observations stored as map keyframes.
The pipeline can include various filters and generators that process the observations, such as downsampling, noise reduction, or feature extraction. The pipeline file can also specify custom plugins to be loaded, which can define new metric map classes or custom filter algorithms.
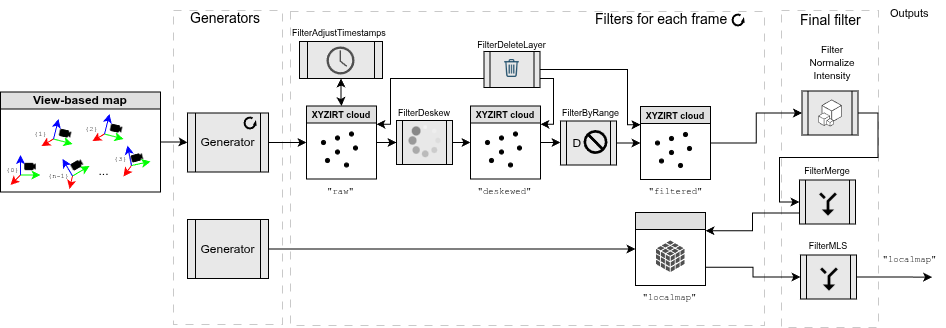
Each pipeline file can contain these sections:
generators:: A list of generators to create maps from each raw observations in each key-frame. If none is provided, the default mp2p_icp::Generator is used, which generates a point cloud from the observation.filters:: A list of filters to apply to each key-frame observations, after generators have been applied. For example, here one typically removes the robot body, de-skew the scan, downsamples the point cloud, and merges the result into one or several final metric map layers used to accumulate the result.final_filters:: An optional list of filters to apply to the final map layers, after all key-frames have been processed.
Refer to example pipeline files sm2mm_*.yaml under the demos directory. Some of them are explained below with a diagram.
3. Example sm2mm pipelines
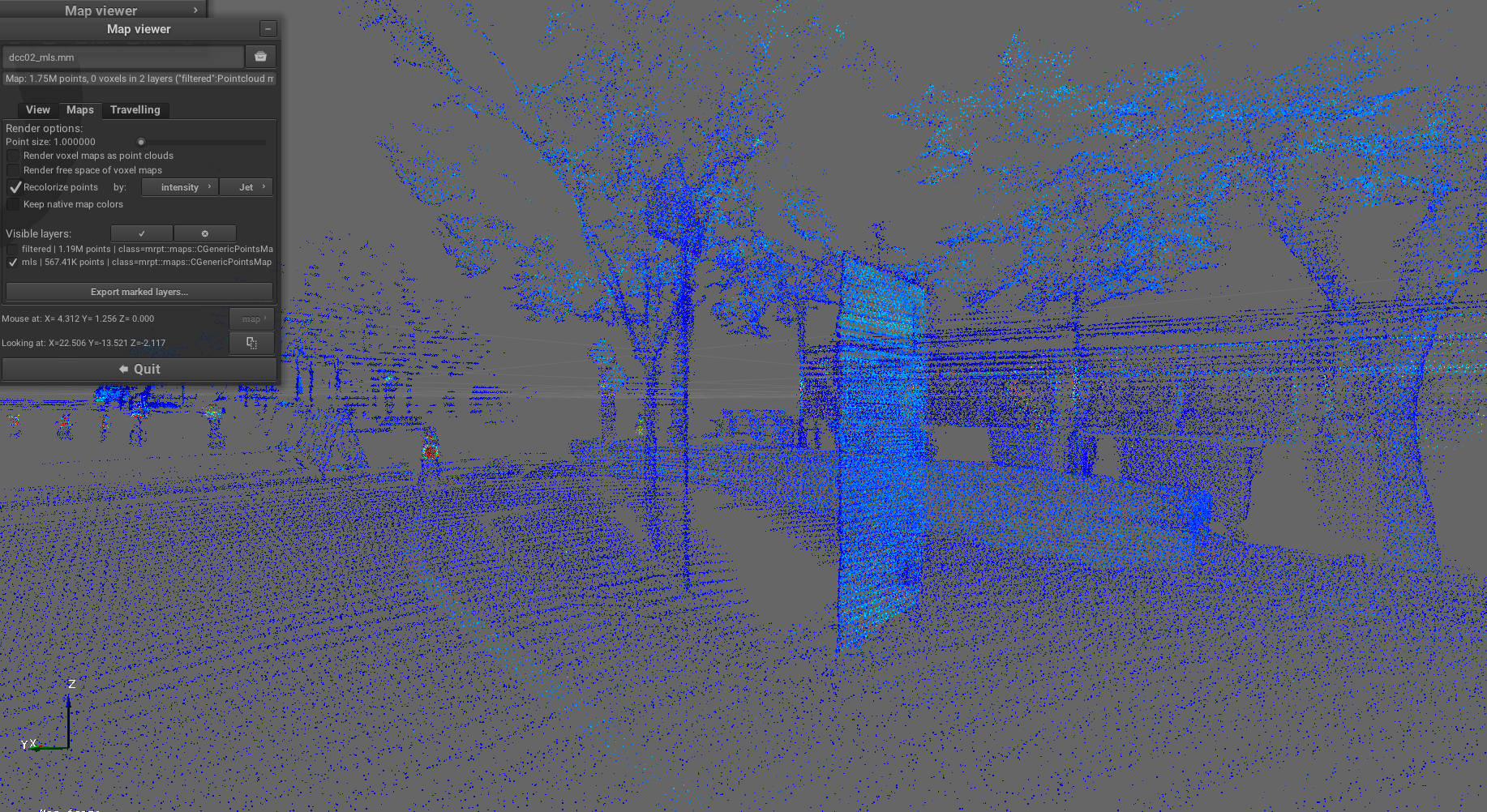
Pipeline: sm2mm_no_decim_imu_mls_keyframe_map.yaml
Purpose: Build a dense (no downsampling) point cloud, using IMU-based motion compensation, then filter the map using the MLS filter,
and store the resulting map into a mola::KeyframePointCloudMap layer named localmap, suitable for MOLA-LIO localization-only mode.
Pipeline YAML code
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Pipeline definition file for sm2mm (simplemap-to-metricmap)
#
# See: https://github.com/MOLAorg/mp2p_icp/tree/develop/apps/sm2mm
#
# Explanation of this particular pipeline:
# - Generators: Default generator creating 'raw', another just creating
# an empty layer "localmap" for GICP MOLA-LIO usage.
# - Filters per observation: Deskew using IMU, remove close points.
# - Final filters at end: intensity normalization, MLS filtering, insert into "localmap"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# --------------------------------------------------------
# 1) Generator (observation -> local frame metric maps)
# --------------------------------------------------------
generators:
# This one will convert all incoming lidar scan observations into pointclouds in layer "raw"
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::Generator
params:
name: "generator_default"
# This one will just create the layer "localmap", expected by the GICP LIO algorithm for localization
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::Generator
params:
name: "generator_localmap"
target_layer: "localmap"
throw_on_unhandled_observation_class: true
process_class_names_regex: "" # None, do not insert directly, but in the final_filters stage.
#process_sensor_labels_regex: '.*'
metric_map_definition:
# Any class derived from mrpt::maps::CMetricMap https://docs.mrpt.org/reference/latest/group_mrpt_maps_grp.html
class: mola::KeyframePointCloudMap
plugin: "libmola_metric_maps.so" # Import additional custom user-defined map classes (search in LD_LIBRARY_PATH)
creationOpts:
max_search_keyframes: 3
k_correspondences_for_cov: 20
insertOpts:
remove_frames_farther_than: 0 # [m]
likelihoodOpts: ~ # none required
renderOpts:
color.A: 0.25 # [0,1] Use this alpha value for points, RGB from colormap
colormap: "cmHOT" # cmJET, cmHOT, cmGRAYSCALE
recolorByPointField: "z" # x,y,z,ring, intensity, ambient, etc.
max_points_per_kf: 100000 # Max number of points to render per keyframe
max_overall_points: 100000 # Max number of points to render overall (e.g. to avoid FoxGlove WS overflow)
#point_size: 1.0 # superseded by visualization.local_map_point_size when run inside MOLA-LIO
# --------------------------------------------------------
# 2) Per local frame filtering
# --------------------------------------------------------
filters:
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterAdjustTimestamps
params:
pointcloud_layer: "raw"
silently_ignore_no_timestamps: false
method: "TimestampAdjustMethod::MiddleIsZero"
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDeskew
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "raw"
output_pointcloud_layer: "deskewed"
method: MotionCompensationMethod::IMU
silently_ignore_no_timestamps: false
output_layer_class: "mrpt::maps::CGenericPointsMap" # Keep all channels: intensity, ring, ...
# These (vx,...,wz) are variable names that must be defined via the
# mp2p_icp::Parameterizable API to update them dynamically.
twist: [vx, vy, vz, wx, wy, wz]
# IMPORTANT: In the context of sm2mm, de-skew happens with points already in global coordinates
# so we need the robot pose to correct points:
points_already_global: true
robot_pose:
[robot_x, robot_y, robot_z, robot_yaw, robot_pitch, robot_roll]
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterByRange
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "deskewed"
output_layer_outside: "filtered"
range_min: 0.0
range_max: 3.0
metric_l_infinity: true # Faster
# Measure distances from the moving robot pose:
center: [robot_x, robot_y, robot_z]
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDeleteLayer
params:
# one or more layers to remove
pointcloud_layer_to_remove: ["raw", "deskewed"]
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3) Final, overall filter pipeline to apply to the whole metric map
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
final_filters:
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Configuration for the Moving Least Squares (MLS) Filter
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterMLS
params:
# The layer containing the point cloud used to compute the MLS surface.
# This is the 'source' cloud for the surface fitting.
input_pointcloud_layer: "filtered"
# The layer where the smoothed/projected points and their normals will be
# stored. If it doesn't exist, it will be created.
output_pointcloud_layer: "mls"
# The class name for output layer if it does not exist and needs to be
# created. Empty means same class than input.
output_layer_class: "mrpt::maps::CGenericPointsMap"
# ====================================================================
# MLS Core Parameters
# ====================================================================
# Search radius (in meters) for finding neighbors around each query point.
# A larger radius results in a smoother but potentially less detailed surface.
search_radius: 0.10
# Order of the polynomial to fit to the local neighborhood.
# 1: Planar fit (fastest, basically a weighted PCA for normals).
# 2: Quadratic fit (standard for curvature/better smoothing).
# 3+: Higher order (can lead to oscillations/overfitting).
polynomial_order: 2
# Minimum number of neighbors required to successfully compute a fit.
# Should be at least 3 for a basic plane (order 1), and more for order 2+.
min_neighbors_for_fit: 10
# ====================================================================
# Smoothing / Projection Method
# ====================================================================
# Method for projecting points onto the fitted polynomial surface.
# SIMPLE: Project point along the normal direction to the polynomial at
# the projected (u,v) location. (Fast and robust).
projection_method: FilterMLS::ProjectionMethod::SIMPLE
# Method for determining which points to smooth/project.
# NONE: Smooth the 'input_pointcloud_layer' itself (standard smoothing).
# DISTINCT_CLOUD: Build the surface from 'input_pointcloud_layer', but
# project the points from 'distinct_cloud_layer' onto it
# (used for upsampling or projection).
upsampling_method: FilterMLS::UpsamplingMethod::NONE
# Required only if upsampling_method is DISTINCT_CLOUD.
# The points in this layer are the ones that will be projected onto the
# surface computed from 'input_pointcloud_layer'.
# distinct_cloud_layer: "sparse_scan"
# ====================================================================
# Parallelization
# ====================================================================
# If TBB is enabled, this is the grain size for parallel execution.
# Smaller values increase parallelism overhead; larger values may leave
# cores idle. Default (1024UL) is typically good.
parallelization_grain_size: 1024
# Specific map for localization with the GICP pipeline
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterMerge
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "mls"
target_layer: "localmap"
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDeleteLayer
params:
# one or more layers to remove
pointcloud_layer_to_remove: ["filtered", "mls"]
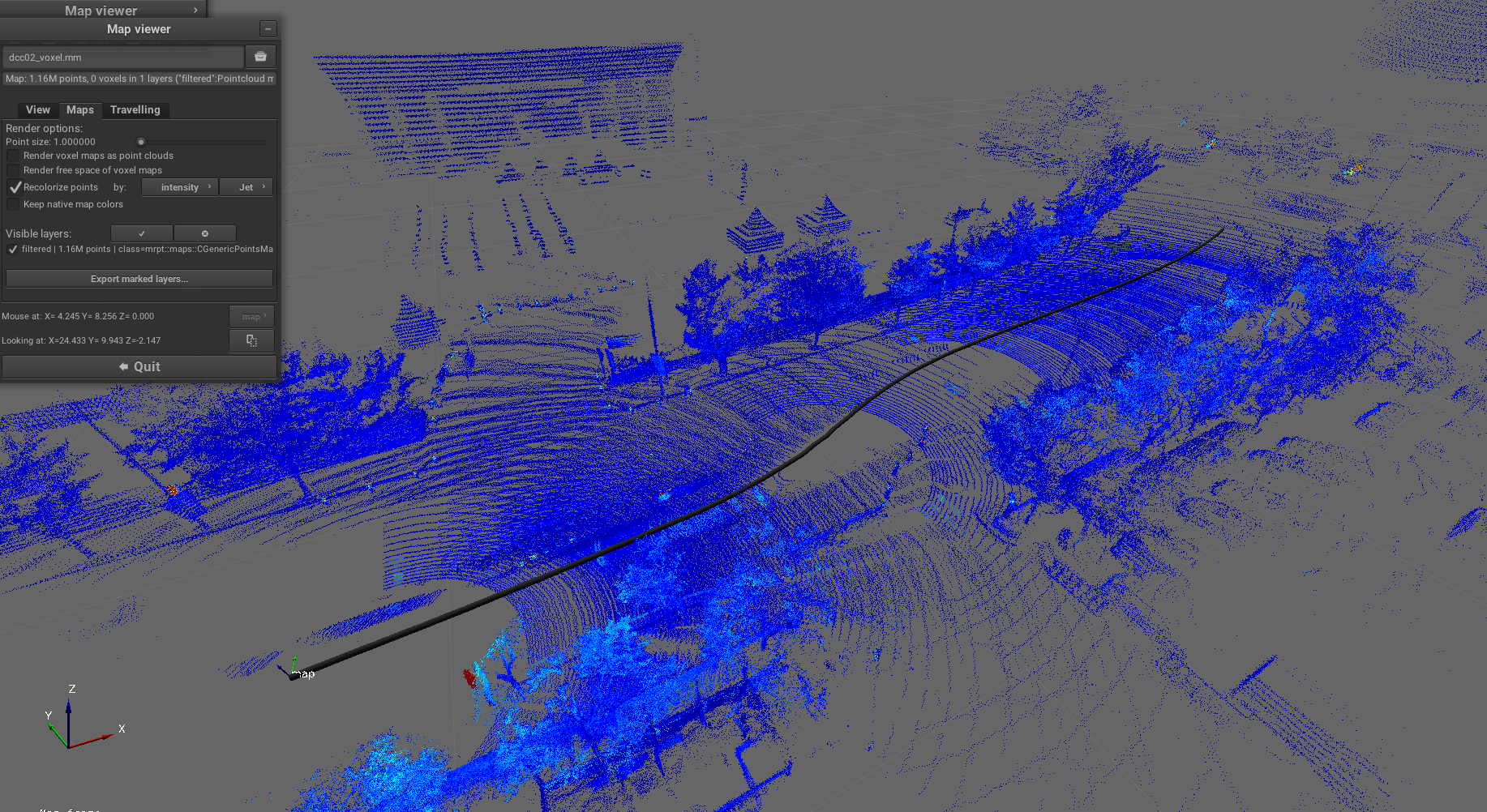
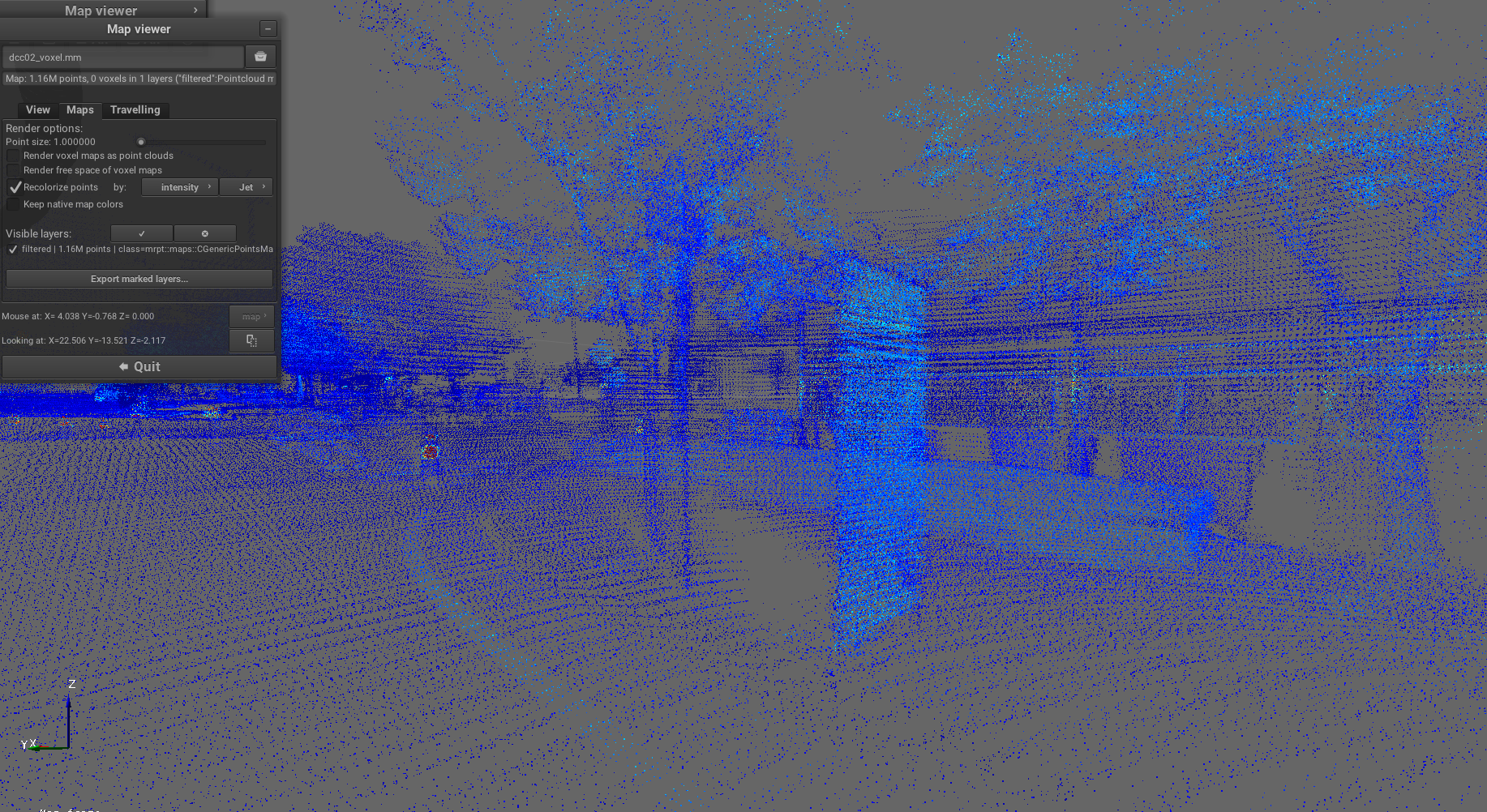
Pipeline: sm2mm_pointcloud_voxelize.yaml
Purpose: Process point clouds by applying voxelization to downsample the data while preserving spatial structure, creating a more memory-efficient representation.
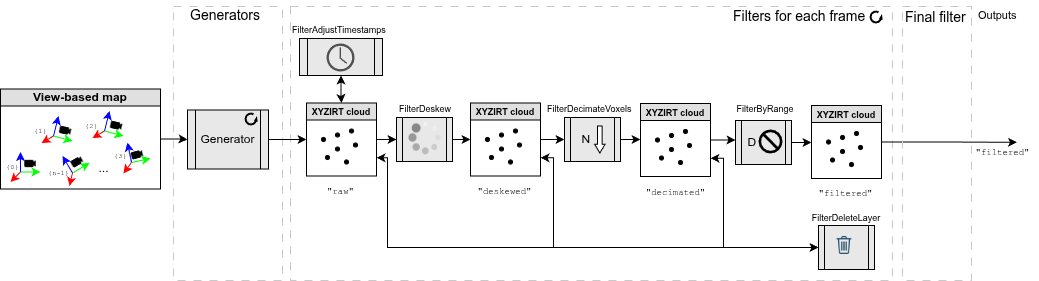
Pipeline YAML code
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Pipeline definition file for sm2mm (simplemap-to-metricmap)
#
# See: https://github.com/MOLAorg/mp2p_icp/tree/develop/apps/sm2mm
#
# Explanation of this particular pipeline:
# - Generators: empty, so the default generator is used (everything in one
# layer named 'raw' with all points).
# - Filters: Just one downsampling filter, with an additional removal of close
# points (e.g. the robot body)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# --------------------------------------------------------
# 1) Generator (observation -> local frame metric maps)
# --------------------------------------------------------
#generators:
# - class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::Generator
# params: ~
# --------------------------------------------------------
# 2) Per local frame filtering
# --------------------------------------------------------
filters:
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterAdjustTimestamps
params:
pointcloud_layer: "raw"
silently_ignore_no_timestamps: true
method: "TimestampAdjustMethod::MiddleIsZero"
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDeskew
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "raw"
output_pointcloud_layer: "deskewed"
method: MotionCompensationMethod::IMU
#silently_ignore_no_timestamps: true # To handle more dataset types
output_layer_class: "mrpt::maps::CGenericPointsMap" # Keep all channels: intensity, ring, ...
# These (vx,...,wz) are variable names that must be defined via the
# mp2p_icp::Parameterizable API to update them dynamically.
twist: [vx, vy, vz, wx, wy, wz]
# IMPORTANT: In the context of sm2mm, de-skew happens with points already in global coordinates
# so we need the robot pose to correct points:
points_already_global: true
robot_pose:
[robot_x, robot_y, robot_z, robot_yaw, robot_pitch, robot_roll]
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDecimateVoxels
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "deskewed"
output_pointcloud_layer: "decimated"
voxel_filter_resolution: 0.02 # [m]
decimate_method: DecimateMethod::FirstPoint
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterByRange
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "decimated"
output_layer_outside: "filtered"
range_min: 0.0
range_max: 5.0
# Measure distances from the moving robot pose:
center: [robot_x, robot_y, robot_z]
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDeleteLayer
params:
# one or more layers to remove
pointcloud_layer_to_remove: ["raw", "deskewed", "decimated"]
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3) Final, overall filter pipeline to apply to the whole metric map
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
#final_filters:
# - (none)
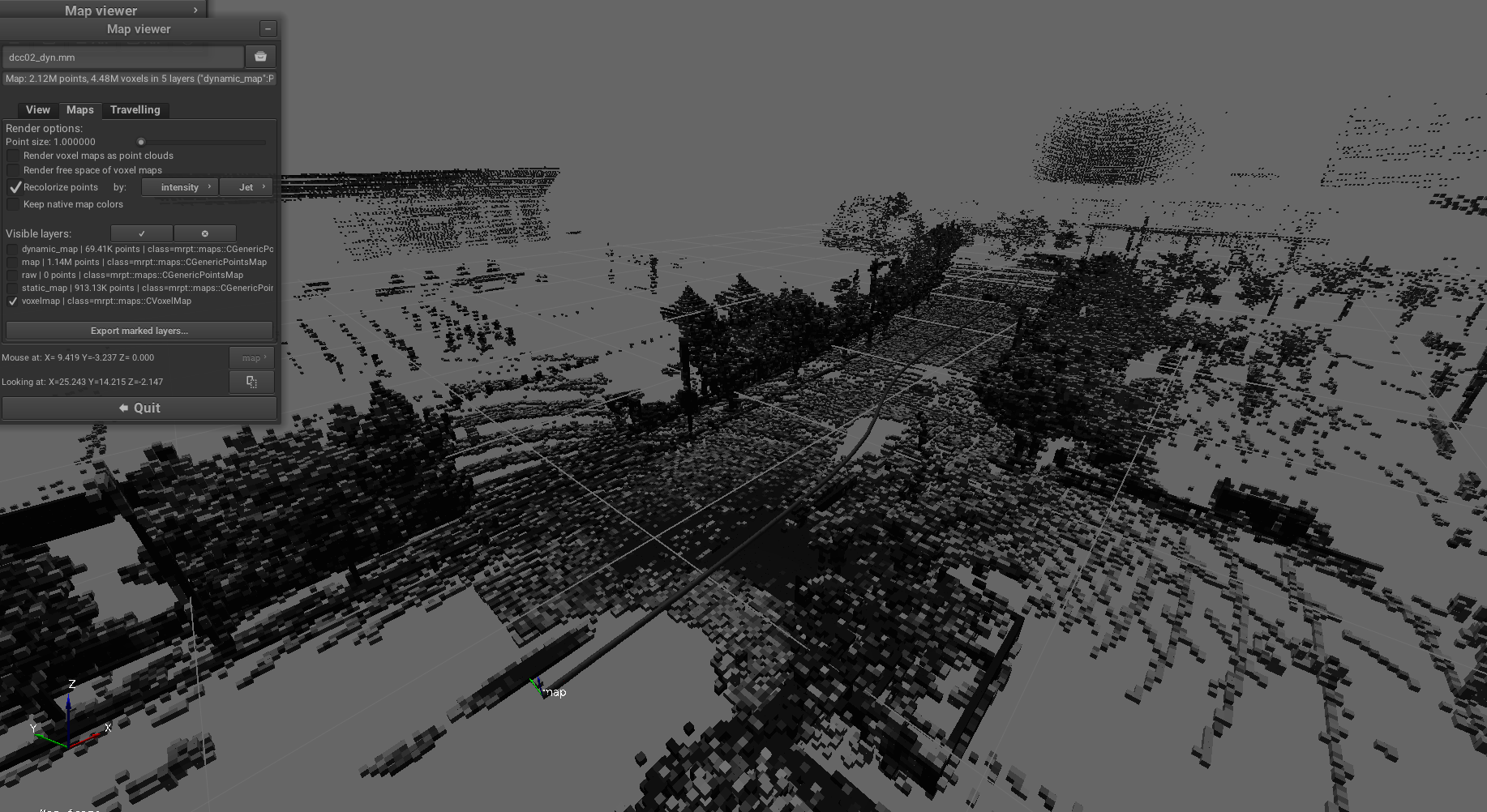
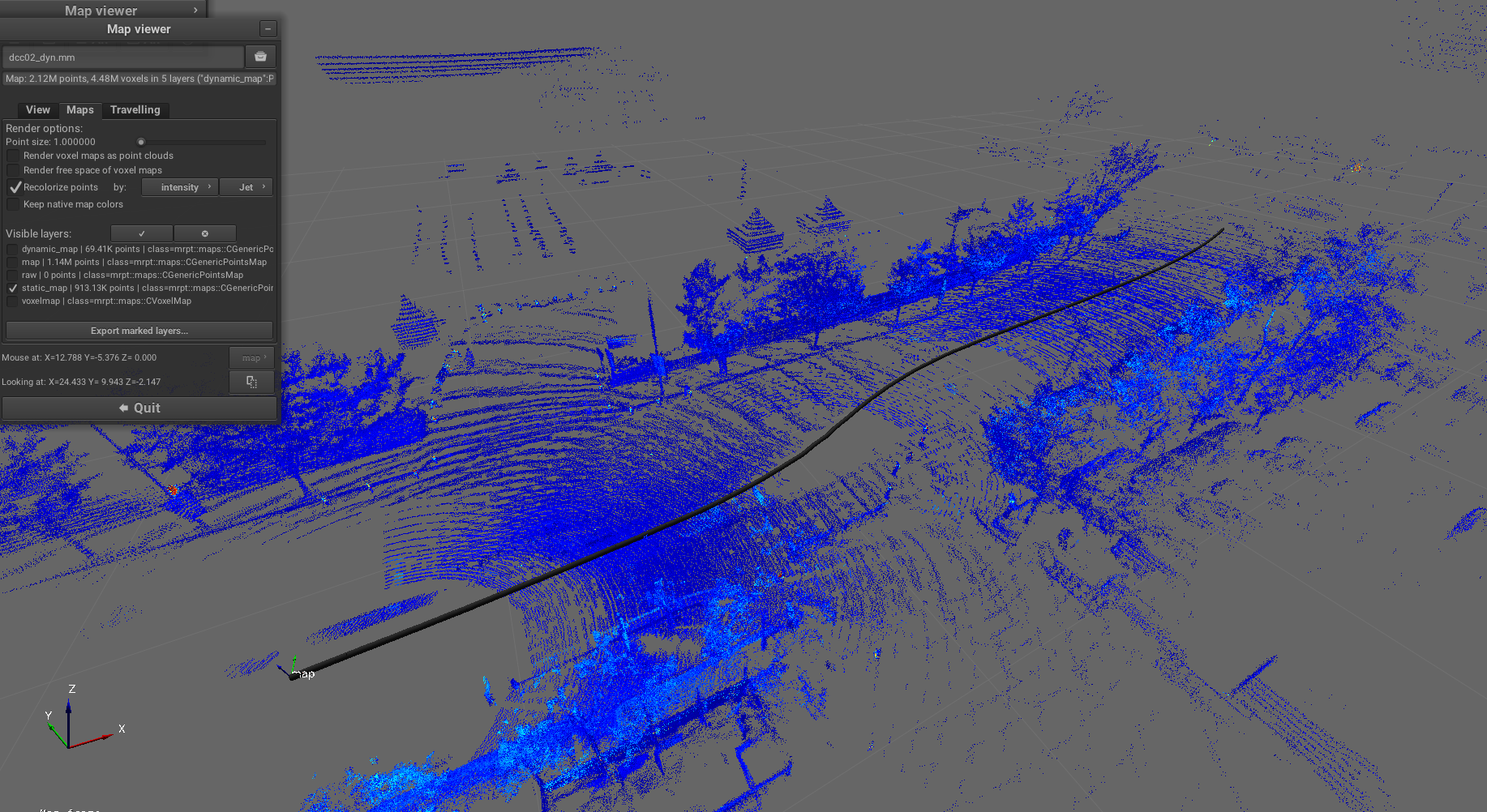
Pipeline: sm2mm_voxels_static_dynamic_points.yaml
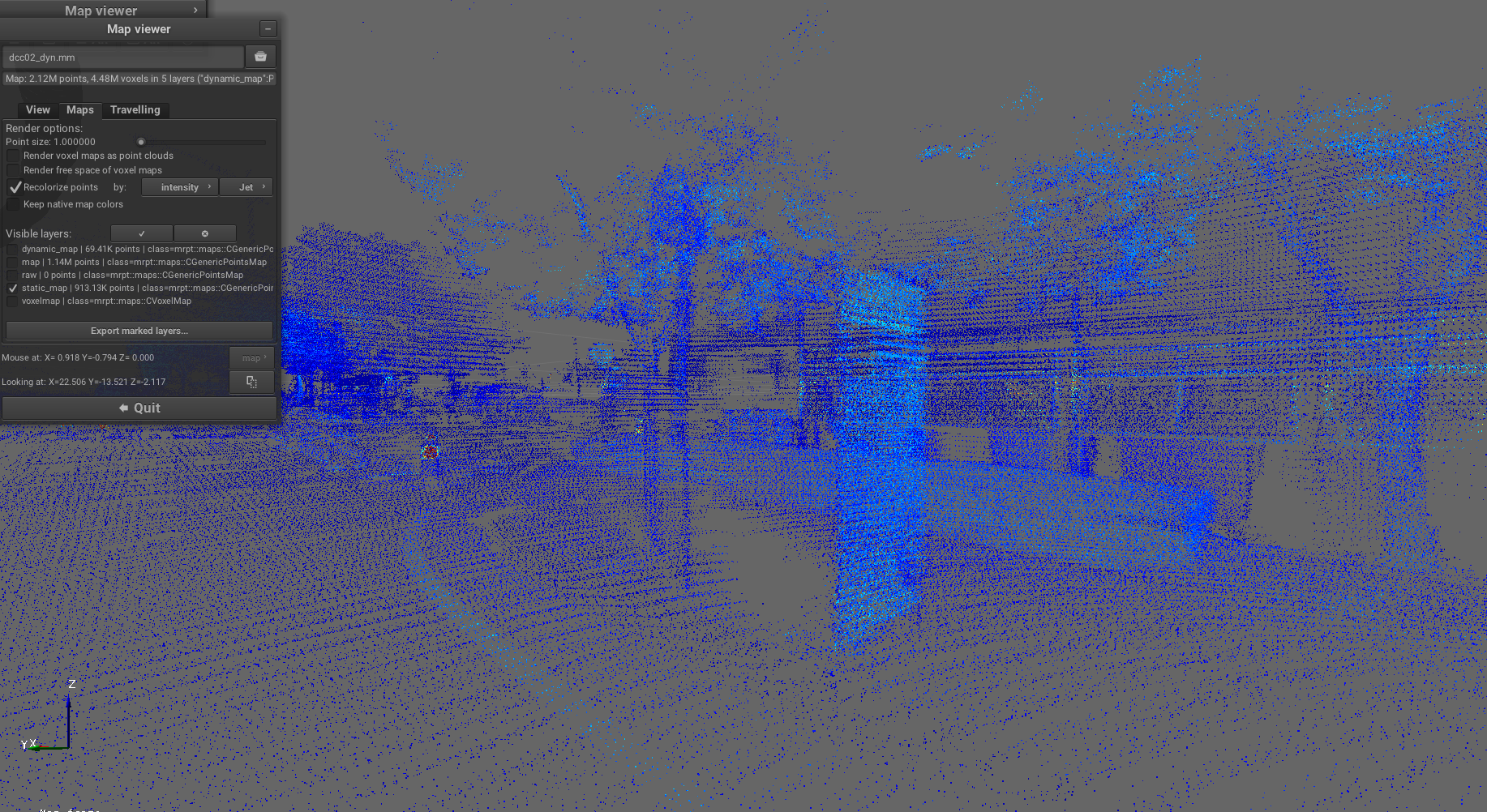
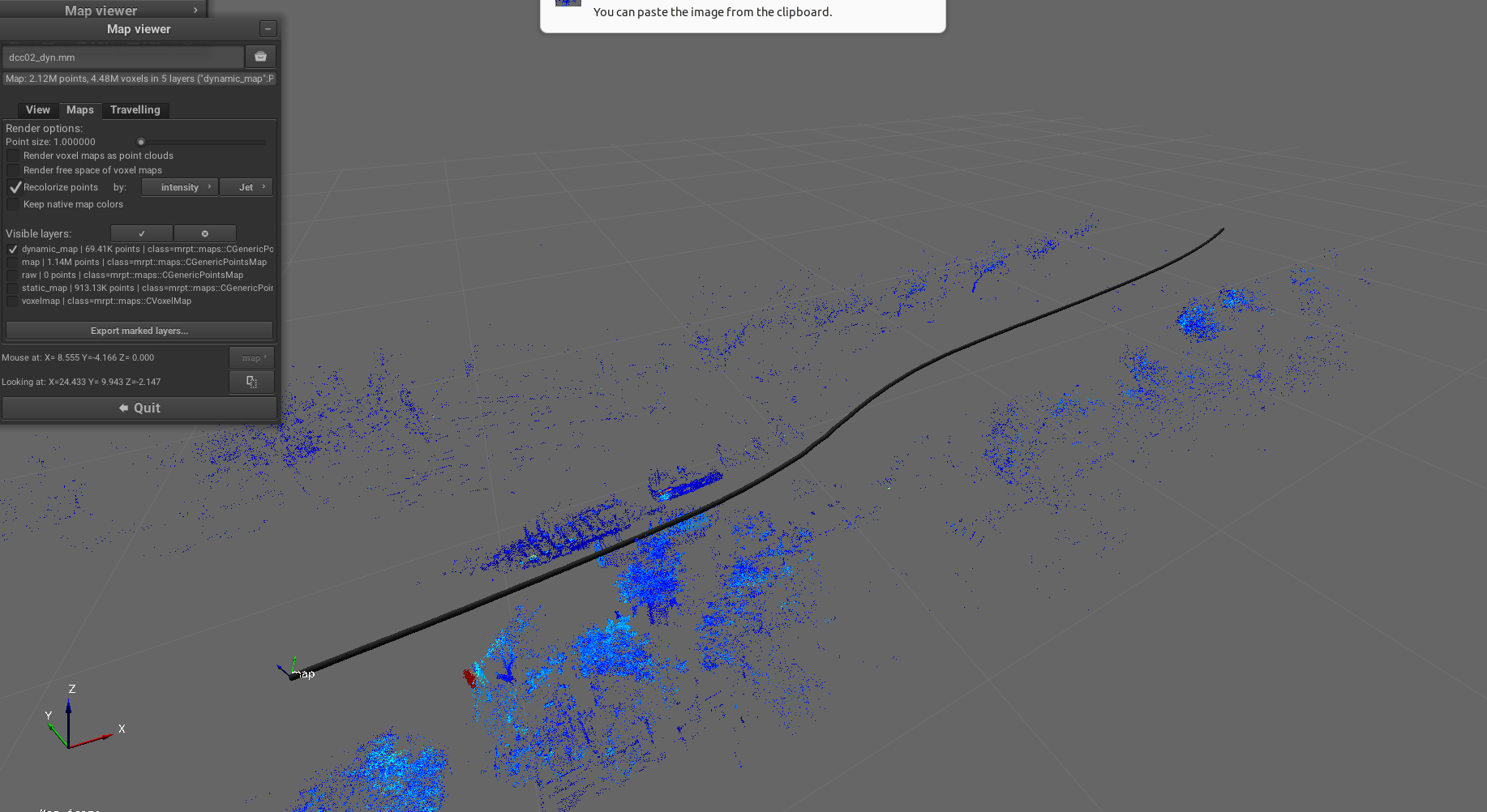
Purpose: Separate point clouds into static and dynamic layers using voxel-based analysis, enabling differentiation between stationary map features and moving objects for robust localization and mapping.
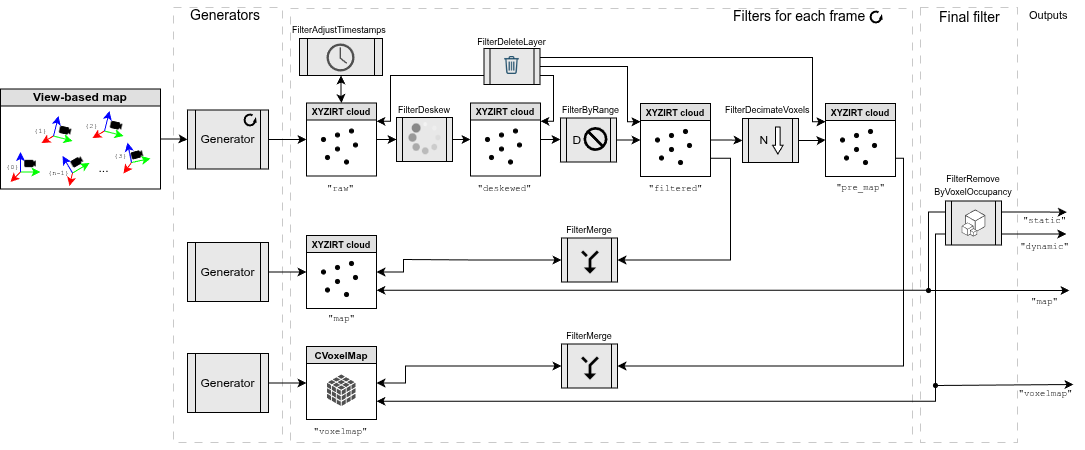
Example result screenshots
Pipeline YAML code
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Pipeline definition file for sm2mm (simplemap-to-metricmap)
#
# See: https://github.com/MOLAorg/mp2p_icp/tree/develop/apps/sm2mm
#
# Explanation of this particular pipeline:
# Creates a 3D voxel map and a point cloud (without downsampling! it may become quite large),
# then in a final step, uses voxel occupancy to tell "dynamic" from "static" points.
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# --------------------------------------------------------
# 1) Generator (observation -> local frame metric maps)
# --------------------------------------------------------
generators:
# This first generator is used to just create the metric map "gridmap" once:
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::Generator
params:
target_layer: "map"
# The default '.*' is replaced by '' (none): do not insert directly any observation,
# since we want to insert them after decimation
process_class_names_regex: ""
metric_map_definition:
# Any class derived from mrpt::maps::CMetricMap https://docs.mrpt.org/reference/latest/group_mrpt_maps_grp.html
class: mrpt::maps::CGenericPointsMap
#plugin: 'libmola_metric_maps.so' # Import additional custom user-defined map classes (search in LD_LIBRARY_PATH)
#creationOpts:
# none required for this class
#insertionOpts:
# none required for this class
#likelihoodOpts:
#renderOpts:
# ...
# This first generator is used to just create the metric map "gridmap" once:
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::Generator
params:
target_layer: "voxelmap"
# The default '.*' is replaced by '' (none): do not insert directly any observation,
# since we want to insert them after decimation
process_class_names_regex: ""
metric_map_definition:
# Any class derived from mrpt::maps::CMetricMap https://docs.mrpt.org/reference/latest/group_mrpt_maps_grp.html
class: mrpt::maps::CVoxelMap
#plugin: 'libmola_metric_maps.so' # Import additional custom user-defined map classes (search in LD_LIBRARY_PATH)
creationOpts:
resolution: 0.25 # [m]
#resolution: $f{0.05*MAX_SENSOR_RANGE} # [m] # You can also use formulas in any numeric field
insertOpts:
#max_range: -1
prob_miss: 0.45
prob_hit: 0.65
clamp_min: 0.05
clamp_max: 0.95
ray_trace_free_space: true
decimation: 1
likelihoodOpts:
decimation: 1
occupiedThreshold: 0.51
renderOpts:
occupiedThreshold: 0.51
freeThreshold: 0.40
generateFreeVoxels: false
# Default generator: convert all observations into a point cloud layer "raw":
# If "raw" does not exist, it will be created
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::Generator
params:
target_layer: "raw"
throw_on_unhandled_observation_class: true
process_class_names_regex: "(mrpt::obs::CObservationPointCloud|mrpt::obs::CObservation3DRangeScan|mrpt::obs::CObservation2DRangeScan)"
process_sensor_labels_regex: ".*"
metric_map_definition:
# Any class derived from mrpt::maps::CMetricMap https://docs.mrpt.org/reference/latest/group_mrpt_maps_grp.html
class: mrpt::maps::CGenericPointsMap
# --------------------------------------------------------
# 2) Per local frame filtering
# --------------------------------------------------------
filters:
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterAdjustTimestamps
params:
pointcloud_layer: "raw"
silently_ignore_no_timestamps: true
method: "TimestampAdjustMethod::MiddleIsZero"
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDeskew
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "raw"
output_pointcloud_layer: "deskewed"
silently_ignore_no_timestamps: true # To handle more dataset types
output_layer_class: "mrpt::maps::CGenericPointsMap" # Keep all channels: intensity, ring, ...
# These (vx,...,wz) are variable names that must be defined via the
# mp2p_icp::Parameterizable API to update them dynamically.
twist: [vx, vy, vz, wx, wy, wz]
# IMPORTANT: In the context of sm2mm, de-skew happens with points already in global coordinates
# so we need the robot pose to correct points:
points_already_global: true
robot_pose:
[robot_x, robot_y, robot_z, robot_yaw, robot_pitch, robot_roll]
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterByRange
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "deskewed"
output_layer_between: "filtered"
range_min: 5.0
range_max: 100
center: [robot_x, robot_y, robot_z]
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterMerge
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "filtered"
target_layer: "map"
robot_pose:
[robot_x, robot_y, robot_z, robot_yaw, robot_pitch, robot_roll]
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDecimateVoxels
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "filtered"
output_pointcloud_layer: "pre_map"
voxel_filter_resolution: 0.20 # [m]
decimate_method: DecimateMethod::FirstPoint
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterMerge
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "pre_map"
target_layer: "voxelmap"
robot_pose:
[robot_x, robot_y, robot_z, robot_yaw, robot_pitch, robot_roll]
# Remove layers not intended for map insertion:
- class_name: mp2p_icp_filters::FilterDeleteLayer
params:
pointcloud_layer_to_remove: ["deskewed", "raw", "filtered", "pre_map"]
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3) Final, overall filter pipeline to apply to the whole metric map
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
final_filters:
- class_name: FilterRemoveByVoxelOccupancy
params:
input_pointcloud_layer: "map"
input_voxel_layer: "voxelmap"
output_layer_static_objects: "static_map"
output_layer_dynamic_objects: "dynamic_map"
occupancy_threshold: 0.7